Evidence Based Outcome Tools for Treating Balance Dysfunction
Learn something now! - Watch the Online CEU Course Trailer

All Access Online CEU for PT, PTA and OT for $189
BEST VALUE - Includes this course and all our online courses
Subscribe Todaytheaters Purchase Now, Instant Online Course Access
Evidence Based Outcome Tools for Treating Balance Dysfunction
This course is only available in our subscription
All Access Online CEU for PT, PTA and OT
$189
All Access Online CEU for PT, PTA and OT Subscription
1 Year Access with Annual Renewal
State specific course completion certificates.
Chat support
Prices are in US dollars- 12 months of access to all online ceu courses, course tests and state approval certificates.
- Meet all your CE requirements. Pre-approved for PT, PTAs in AK, AL, AZ, CA, CO, CT, DC, DE, GA, HI, IA, ID, IL, IN, KS, MA, ME, MI, MO, MS, MT, NC, ND, NE, NH, NM, NV, NY, OR, PA, RI, SC, SD, TN, TX, UT, VA, VT, WA, WI, and WY.
- AOTA approved.
- Designed for Physical Therapists, Occupational Therapists, Athletic Trainers and Assistants.
- Access to future courses and content.
- Start, stop and resume, right where you left off in a course.
- Real patient interviews.
- Medical expert contributors.
- 3D anatomy and medical illustrations.
- Easy to use learning system for fast access to your courses.
- Award winning content.
- Top instructors teaching evidence based skills and techniques.
Why should a physical therapist, occupational therapist or athletic trainer take this balance dysfunction vestibular continuing education course?
According to the CDC, there are currently over 29 million falls and 3 million emergency room visits per year. Physical and occupational therapists evaluate fall risk by ruling out potential sources of dizziness and instability. The vestibular rehabilitation evidence-based clinical practice guidelines identify essential tools and skills for proper assessments and treatment programs. Therapists can rule out specific causes of the symptoms such as BPPV, muscle imbalance, neurological deficits, and other neuromuscular disorders that can lead to instability, falls, and injury.
The information presented in this balance dysfunction continuing education course provides the clinician with evidence-based validity for the tools and techniques utilized to evaluate and treat the imbalanced patient.
Rehab clinical tools instructed in this vestibular rehab CE course to enhance your functional outcomes.
- Evidence-based research and clinical applications provide an encyclopedia of information for the clinician to master evaluation and treatment techniques for balance and vestibular disorders.
- In-depth explanation and demonstration of vestibular spinal tracts and testing the vestibulo-ocular reflex
Specific instruction that will enhance your understanding and ability to deliver better patient care.
- Many of the functional assessment tools presented in this course and utilized in today’s rehab environment have been researched and developed by Dr. Wrisley.
- Standard testing and treatment techniques used within the Clinical Practice Guidelines
- Vestibular, neurological, and orthopedic causes of imbalance are discussed, including pathologies such as stroke, Multiple Sclerosis, Parkinson’s Disease, cerebellar dysfunction, orthopedic dysfunction, and vestibular dysfunction
Features unique to this vestibular rehabilitation continuing education course
- Demonstration and description of the most relevant tests utilized to assess function, and strategies for identifying tests for varying levels of function, from the lower-level to the higher-level athlete
- Demonstration and description of the most relevant treatment strategies for balance and postural training
- Evidence -based information to determine appropriate evaluation tools and treatment techniques that benefit specific particular needs within their environment.
- Special BPPV section which includes explanations of BPPV tests and interpretations, the efficacy of maneuvers, and clinical pearls when performing techniques.
Professional Accreditation
This is an intermediate level course applicable for PT, PTA, OT, AT. Physical Therapy Accreditation: For specific state information use the accreditation verification menu and select your state of license. AOTA: provider #4487, Occupational therapy professional development activity: Occupational Therapy Service Delivery, evaluation and intervention, and Foundation Knowledge: human body, development, and behavior. Athletic Trainers: BOC provider #P2047, category A. This course has not been submitted for Evidence-Based BOC approval.
fact_check Accreditation Verification
Online CEU Course for PT, PTA, OT State Accreditation
Course Objectives

This course will provide the participant with to ability to:
- Compare and contrast the systems underlying balance.
- Discuss the differences in the balance system with different pathologies, as well as identify the changes that occur across the lifespan, especially with aging.
- Differentiate different causes of imbalance, employ appropriate outcome measures, and implement treatment.
- Perform examinations and interventions for balance dysfunction in patients with orthopedic problems, neurologic problems, and vestibular dysfunction. Utilize the appropriate evidence-based test/tools that are appropriate for specific situations.
- Perform a thorough neurological examination.
- Identify the proper function of cranial nerve 8 when performing specific tests.
- Identify which tools are most appropriate to use for evaluation and treatment when assessing balance, gait, and function.
- Develop evidence-based intervention for patients with vestibular, neurologic, orthopedic, and cervicogenic dysfunction.
- Discuss BPPV tests and interpretations, efficacy of maneuvers, keys to performing techniques for successful results and evidence-based expected outcomes.
- Properly perform the following tests: Canalith Repositioning Maneuver, Dix-Hallpike maneuver, horizontal canal repositioning, Brandt-Daroff exercises, Gufoni maneuvers,and Epley Semont maneuver.
- Discuss common causes of vestibular balance dysfunction, cervicogenic dizziness, and migraine-related vestibulopathy.
- Develop intervention strategies that are relevant to the patient with balance dysfunction, total joint arthroplasties, lumbar spine dysfunction, and vestibular dysfunction.
- Discuss the pathological process that involves BPPV, cervicogenic causes of dizziness and imbalance, concussion, and traumatic brain injury.
- Develop higher-level balance training, fall risk assessment, and intervention programs for the higher-level athlete or individual.
- Develop fall risk assessment programs and intervention programs for varying levels of function, from lower-level to the higher-level athlete.
Balance and Postural Control

- What is Balance?
- What factors contribute to balance?
- What are the different movement strategies
- How does cognition contribute in our ability to balance?
- Thinking about postural control as a loop
- Factors that affect both the center of gravity and the limits of stability
- The information from the visual system, the vestibular system, and the somatosensory system
- What happens if an individual has a problem within a sensory system?
- Which body movements are necessary to keep us upright?
- The consequence of peripheral neuropathy
- Dealing with an aging vestibular system in your patients
- Problems with the motor control system
- Parkinsons Disease, Down Syndrome and motor control
- Managing with a loss of anticipatory postural control
- Abnormal postural control and sensory organization
Vestibular Anatomy and Physiology
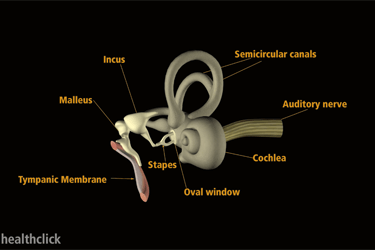
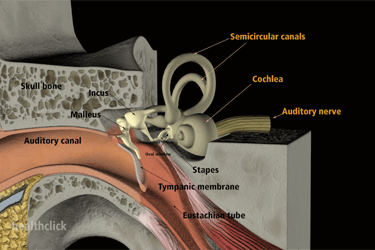
- Learning about vestibular anatomy and physiology and how it contributes to balance and postural control
- Where is the peripheral vestibular system?
- Learning about the semicircular canals
- The common crus Aplasia and its connection to the canals of the ear
- What are the semicircular canals so interesting?
- The ampulla and the sensory organs for the inner ear
Vestibulo-Ocular Reflex and Visual System
- Understanding the lateral vestibular spinal track
- Understanding nystagmus and eye movement patterns
- Measuring gain in the vestibulo-ocular reflex
- The vestibular nuclei and sending and receiving information from the cerebellum.
- Understanding the visual field and deficits
- Different types of eye movements, Conjugate eye movements, lazy eye
- Vergence and Gaze stabilization
Vestbular Examination Overview

- The cardiorespiratory system, cognition, the musculoskeletal system, sensory system, orientation in space, and movement strategies
- The importance of the medication review
- What is the social history of this patient
- The Montreal Cognitive Assessment
- Looking at the integumentary system
- Sensation: Light touch, pinprick, vibration using the 128-Hz tuning fork, monofilaments, and proprioception
- The Dix-Hallpike Maneuver
- Alignment from all directions-anterior, posterior, and lateral
- Understanding intersegmental mobility
- The FACT Test
- The Melbourne Edge Test
- What are Saccades?
- Understanding and testing test optokinetic nystagmus
- Examining convergence, and the ability of the eyes to move symmetrically
- Active and passive VOR
- The Head Impulse Test
- Activities-specific Balance Confidence Scale
- Modified Clinical Tests for Sensory Interaction and Balance
- Tests for gait and balance such as Romberg and the Sharpened Romberg
- The Single Limb Stance Test
- The 30-Second Chair Stand Test
- Five Times Sit to Stand
- The Four Square Step Test
- The Multi-Directional Reach Test
- The Berg Balance Scale
- Tinetti Performance Oriented Mobility Scale, or the POMA
- The Mini-BES Test
- Dynamic Gait Index
- The Time Up and Go
- The Functional Gait Assessment
- The Six-Minute Walk Test
- Fall risk assessment-Morse Fall Scale, the Hendrich II Fall Risk Assessment, and Stratify, the St. Thomas Risk Assessment Tool
- Test higher-level balance - the Star Balance Test, the Balance Error Scoring System, or the High-Level Mobility Assessment Tool
- The Y Direction Test
- Fall risk assessments for home health-The Missouri Alliance for Home Care, or the MAHC-10
- High-Level Mobility Assessment Tool
- The Community Balance and Mobility Scale
Different Factors that Can Lead to Balance Dysfunction

- Motor problems with range of motion, strength, motor control, posture, and intersegmental mobility
- problems with reflexes, sensation, radicular pain, and spasticity
- Decreased cervical spine mobility and its association with the vestibular system
- Strength problems and your balance strategies
- Intersegmental mobility, and patients with lumbar, cervical, and thoracic spine dysfunction
- Relating Reflexes - spasticity or rigidity and CNS Dysfunction
- Hypo-reflexive and association with the peripheral nervous system
- Radicular pain coming with the inner segmental mobility
- Problems with somatosensory information
- Modified Clinical Test of Sensory Interaction Imbalance
Vestibular Causes of Imbalance

- Peripheral and central causes of dizziness from the vestibular system
- Migraine-related vestibulopathy
- Multiple Scherosis and dizziness
- Unilateral vestibular loss, or hypofunction
- Vestibular labyrinthitis and inflammation of the whole labyrinth
- Infarction of the labyrinthine artery, trauma, demyelinating disease, or Meniere’s disease
- Perilymphatic fistula - episodic vertigo, imbalance, and sensorineural hearing loss
- Bilateral vestibular loss and loss of function in the vestibular system in both sides
- BPPV and the most common form of dizziness
- Problems with the vestibular nuclei, the cerebellum, or other vestibular pathways
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo
- The displacement of the otoconia
- Theories of pathophysiology for BPPV
- Symptoms of the BPPV
- The etiology of the BPPV
- The diagnostic criteria for BPPV
- different tests to diagnose BPPV
- Posterior canal involvement
- Torsional eye movements
- video nystagmography or Frenzel lenses
- The Roll Test tests for horizontal canal BPPV
- Canalithiasis in the posterior arm
- Horizontal canal involvement with canalithiasis
- Treating BPPV - liberatory maneuver, or the Semont maneuver, for posterior or anterior canal
- The Roll maneuver for the horizontal canal
- the Barbecue, or the Lempert
- Appiani, or the Gufoni maneuvers
- Canalith Repositioning Maneuver
- Outcomes after Canalith Repositioning Maneuver
- Brandt-Daroff exercises
- Difficulties in diagnosing BPPV
- Understand BPPV symptoms that recur
- Who is the Canalith Repositioning and the Dix-Hallpike appropriate?
- What are some contraindications?
- Dix-Hallpike for patients with hip replacement
Evaluation Lab Techniques : Demonstrations and Descriptions

- Reflexes are important to test
- Reflexes are graded on a scale of zero to four
- Testing the triceps reflex
- Where do hyperactive reflexes come from?
- Performing sensory testing
- Weinstein Enhanced Sensory Test
- Using the 128-Hz tuning fork
- Testing the cranial nerves
- Testing saccades
- Testing for convergence
- Optokinetic nystagmus
- Vestibular nystagmus
- Testing cranial nerve eight
- Demonstration of tests for the Balance System
- Learning to perform a Sharpened Romberg test
- Learn the Functional Gait Assessment
- Demonstration of the High-Level Mobility Assessment Tool
- Execute a Mini-BESTest
- Learn to execute the Modified Clinical Test of Sensory Interaction and Balance
Treating the Dysfunction

- The intervention is based on impairment rather than diagnosis
- Visual biofeedback devices
- Anticipatory balance control
- Upweighting the vestibular system
- Promote the use of somatosensory inputs
- Treatment for improving balance strategies
- Intervene at the functional task level
- Putting all this information together
Treatment Techniques: Demonstrations and Descriptions

- Creating a balance training treatment program
- Treatment plan progression
Patient Case Study

- 62-year-old post total knee arthroplasty
- This patient will inevitably fall
- How would we evaluate, develop a plan and deliver treatment?
Course Test - Evaluate your knowledge
- Use the Healthclick proprietary online education system which provides the online student with:
- Worldwide access to high definition video, anatomical animations and images, and written information
- The highest quality film in the industry, you can see the difference!
- Stop and resume within a course, the Healthclick system will optimize your course based on your device, connection and remembers where you left off.
- Real-time course updates. We are always adding to each courses, updating content, adding animations, these are not static courses!
- Evaluate your knowledge with the course test on any device.
- Print your state course certificate for CE credit.
- Take the online test as many times as need in order to achieve a 70 % or greater score.
Responsible CME® - Online CEU Course Testimonials
67.225.255.111Very informative and interesting. I hope to attend the live course in future to add to my knowledge. -- Kirsten, PT
Excellent material with good, clinical applications -- Andrea, PT
I thoroughly enjoyed this course and plan to study the material several times as it is very pertinent to developing good treatment plans for balance -- Gillian, Physical Therapist
Highly recommended take any course she has. -- Michele, Physical Therapist